Backup & Disaster Recovery
Expect the best. Prepare for the worst.

Disaster Recovery
No one expects data corruption or loss, but it is far less expensive to maintain a backup than to have to re-create it from scratch.
GMX TEC Cloud provides automatic backup solutions!
Why Move Backup and Disaster Recovery To The Cloud?
Backup and Restore
Protect data without the need for expensive on-site hardware and administrative overhead. Cost-effective data recovery enabled by an enterprise-grade multi-region public cloud infrastructure.
Disaster Recovery (DR)
Eliminate the need to replicate your production system in full at a secondary company managed
Test and Development
Test/Dev replicated systems can be instantly spun-up as needed, on demand, with no dedicated hardware or software for greater flexibility and speed.
Data Analytics
Analyze backed up data to understand risks and challenges around dormant data, storage growth, and data classification. A cloud storage model can increase visibility into existing data which can then be better leveraged for additional business value.
Converged Architecture
Converge multiple workloads together in a ‘single pane of glass’ while gaining the assurance that your data, stored on the public cloud infrastructure, adhere to global data privacy regulations.
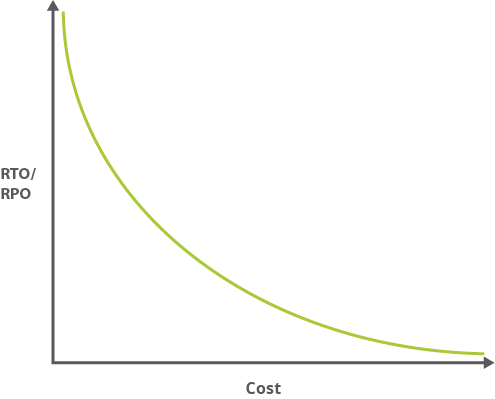
Recovery Time Objective
RTO
The recovery time objective (RTO) is the maximum tolerable length of time that a computer, system, network, or application can be down after a failure or disaster occurs.
There are three primary ways to reduce the recovery time of servers:
-
Have the servers in affinity groupings that logically go together, either by tiers or by service or application support.
-
Integrating the orchestration and replication tools for administrative efficiency
-
Thoroughly and routinely perform failover tests. Perfect the boot order, re-
ip addressing, and scripts well ahead of when an outage occurs. Have the failover push-button ready.
Recovery Point Objective
RPO
The recovery point objective (RPO) is the age of files that must be recovered from backup storage for normal operations to resume if a computer, system, or network goes down as a result of a hardware, program, or communications failure. The RPO is expressed backward in time (that is, into the past) from the instant at which the failure occurs, and can be specified in seconds, minutes, hours, or days. It an important consideration in disaster recovery planning (DRP).
The RPO gives systems designers a limit to work to. For instance, if the RPO is set to four hours, then in practice, off-site mirrored backups must be continuously maintained – a daily offsite backup on tape will not suffice.
Assess
Risk
2
Define RPO and RTO
3
Assign
Tasks
4
Manage Sensitive Data
5
Test Plan Regularly
Before designing a DR plan, we conduct a thorough risk assessment to
This step is critical because it is where we determine what kind of DR plan is required.
GMX will help you determine who needs to do what in the event of a disaster.
Every organization has sensitive data, whether it be proprietary resources,
Once you have a DR plan in place, we will assist in testing it regularly.
Multi-Site / Multi-Region Architecture
GMX TEC introduces a multi-region architecture that can provide higher availability than deploying to a single region.
If a regional outage affects the primary region, you can use Traffic Manager to fail over to the secondary region.
This architecture can also help if an individual subsystem of the application fails.
There are several general approaches to achieving high availability across regions and we
are going to explore them together.
Implement a recovery strategy
Implementation & Testing
GMX TEC offers a full package on recovery strategies.